Android provides a default Android framework implementation that includes support for various Wi-Fi protocols and modes, including:
- Wi-Fi infrastructure (STA)
- Wi-Fi hotspot (Soft AP) in either tethered or local-only modes
- Wi-Fi Direct (p2p)
- Wi-Fi Aware (NAN)
- Wi-Fi RTT (IEEE 802.11mc FTM)
An application using Wi-Fi services directly communicates with the various Wi-Fi services through Binder. The Wi-Fi services run in the System Service and communicate with the HAL over the provided HIDL and AIDL interfaces. This diagram shows the general structure of the Android Wi-Fi stack.
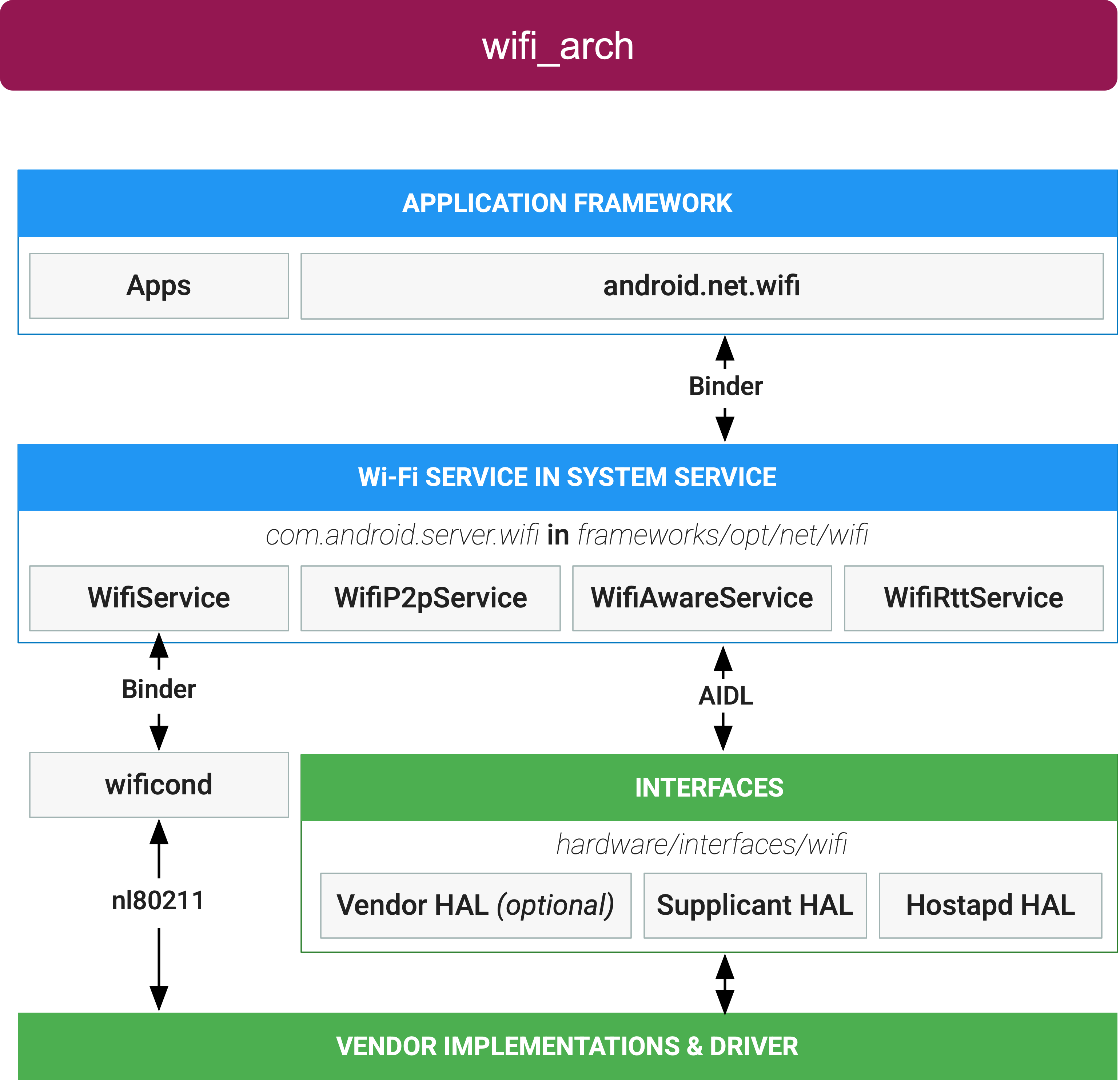
Figure 1. Android Wi-Fi architecture
Application framework
At the application framework level is application code, which uses the various
android.net.wifi
APIs to interact with the Wi-Fi framework and hardware. Internally, this code
calls the Wi-Fi process through the Binder IPC mechanism.
Wi-Fi services
The Wi-Fi services run in the System Service, and are located in
packages/modules/Wifi/service/. The Wi-Fi service communicates with the
Wi-Fi HAL over AIDL.
There are various Wi-Fi services:
- Wi-Fi Service: Primary mechanism for controlling Wi-Fi infrastructure modes (both STA and AP).
- Wi-Fi P2P Service: Manages the Wi-Fi Direct mode.
- Wi-Fi Aware Service: Manages the Wi-Fi Aware mode.
- Wi-Fi RTT Service: Manages the IEEE 802.11mc FTM functionality.
The Wi-Fi framework also includes a standalone process, wificond, located
at system/connectivity/wificond. The wificond process communicates with
the Wi-Fi driver over standard nl80211 commands.
Wi-Fi HALs
The Wi-Fi framework has three Wi-Fi HAL surfaces represented by three different interfaces: Vendor HAL, Supplicant HAL, and Hostapd HAL.
For details about implementations of the various HALs, see Wi-Fi HAL.
