Hardware assessment involves defining three haptic effects, labeled Effects 1, 2, and 3 for this specific assessment.
Effect 1: Predefined short haptic constants
The
VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK
constant is the baseline effect or common denominator in the HAL-API mapping
provided in Map constants between HAL and API
. It's mapped with the most used effect, HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_PRESS
. Assessing this effect helps determine the readiness of your target device for
clear haptics.
Effect 2: Short custom haptic effect
The
VibrationEffect.createOneShot(20,255)
constant is for custom haptic effects. For short, single custom impulses,
20 ms is the recommended maximum threshold to define duration. A single
impulse longer than 20 ms isn't recommended because it's perceived as a
buzzy
vibration.
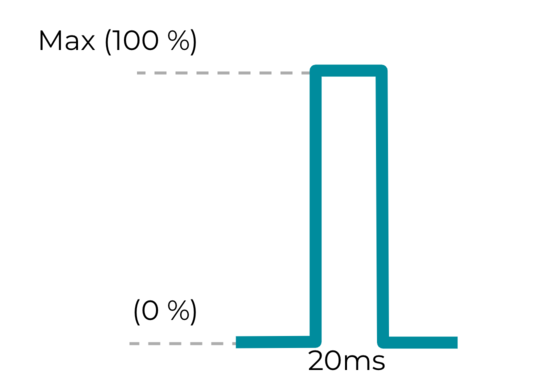
Figure 19. Short custom haptic effect
Effect 3: Long custom haptic effect with amplitude variation
The VibrationEffect.createWaveform(timings[], amplitudes[], int
repeat)
constant is for long custom effects with amplitude variation. The ability to
produce varying amplitudes for custom haptic effects is one of the indicators to
evaluate the device's capabilities for rich
haptics. The
recommended timings [] and amplitudes [] are {500, 500} and {128, 255},
respectively, which presents an increasing trend of amplitude from 50% to 100%,
with a 500 ms sampling rate.
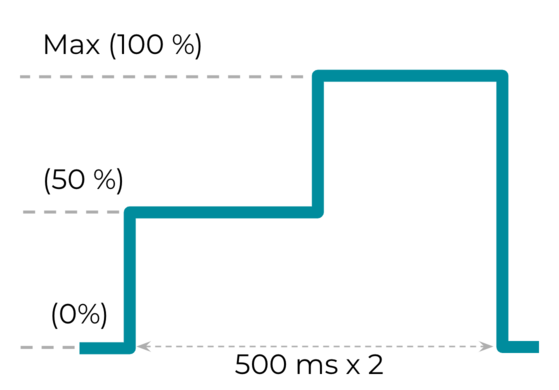
Figure 20. Long custom haptic effect with amplitude variation
To check the hardware capabilities of amplitude control for Effect 3, use the
Vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl()
method. The result has to be true to execute
VibrationEffect.createWaveform
with varying amplitude as intended.
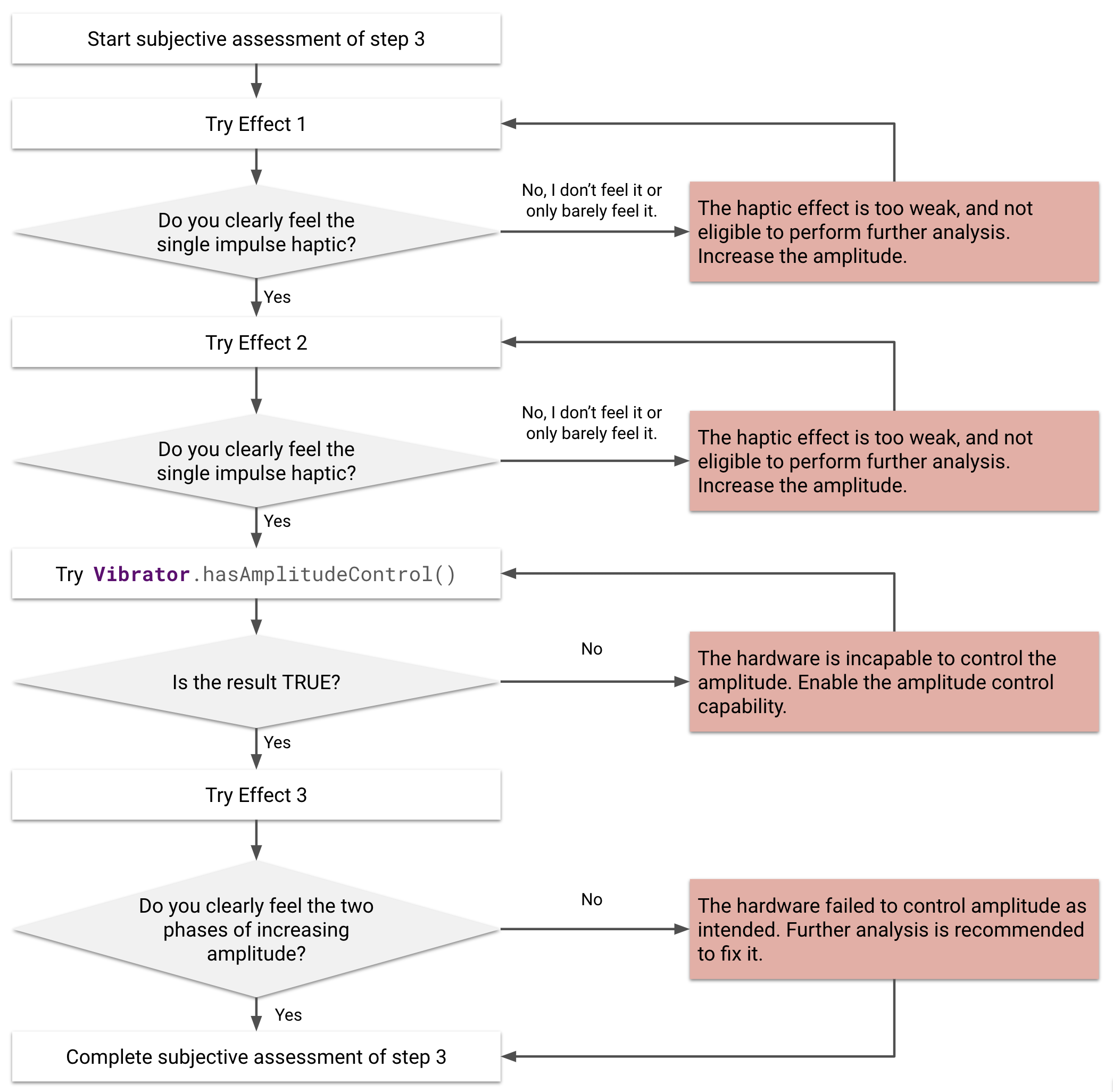
Figure 21. Subject assessment of haptic effect 1, 2, and 3
Perform a subjective assessment
For a quick coherence check, perform a subjective assessment first. The goal of the subjective assessment is to observe the amplitude of the haptic effects to determine whether the device can generate haptics with human-perceptible amplitudes.
A specific question structured around this notion looks like this: Can the device produce perceptible haptic effects to the users as expected? Answering this question helps you avoid failed haptics, including imperceptible haptics that users can't feel, or unintended haptics where waveforms don't produce patterns as intended.
Perform an advanced assessment
Performing advanced quality assessments is highly recommended. Advanced quality assessments characterize quantifiable attributes of haptic effects to implement quality haptics. When finished, device manufacturers should be able to diagnose the current haptic status, which means they can set goals to improve the overall quality. See Hardware assessment.
