The audio framework CTS-V tests require requires human intervention and some external hardware, including an audio loopback dongle, a USB-to-analog adapter or interface, a USB reference microphone, and external speakers.
To access the tests on this page, see General instructions.
Loopback latency test
The audio loopback latency test measures the total time from the generation of an audio signal to the detection of that same signal. This time measurement is used as a proxy for measuring the overall latency of the audio system.
The latency is measured over several data paths, including:
- Speaker to microphone
- USB audio output to input
- 3.5 mm analog output to input if the device supports it
Select peripherals
If the device has a 3.5 mm analog headset jack, you need an audio loopback dongle or plug. The dongle contains contains electronics that route an audio output signal back to the audio input.
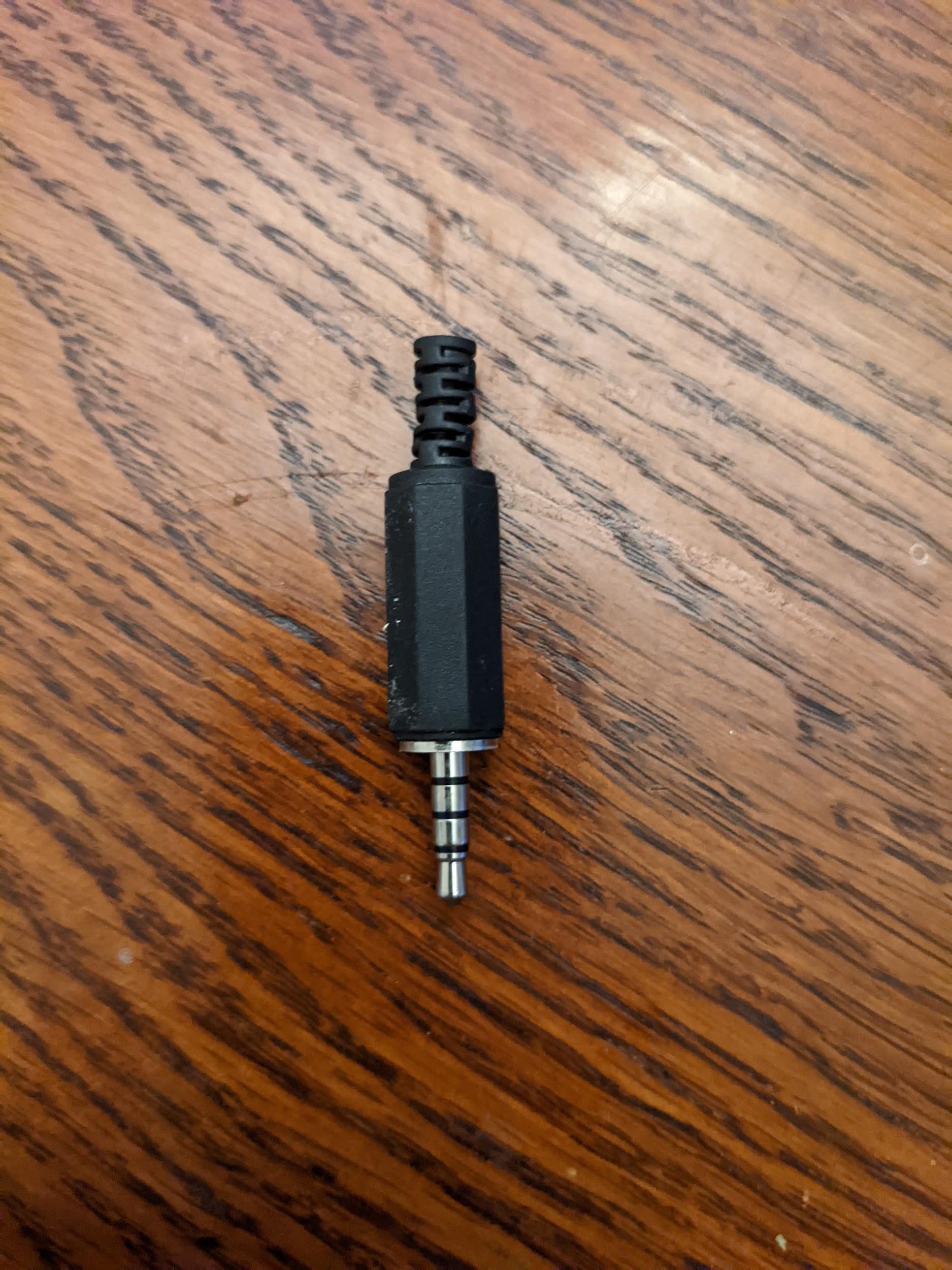

Figure 1. Audio loopback plug.
For testing USB, you have two options. The first option is to use an audio loopback dongle connected to a USB-to-analog adapter, shown in the following figure:
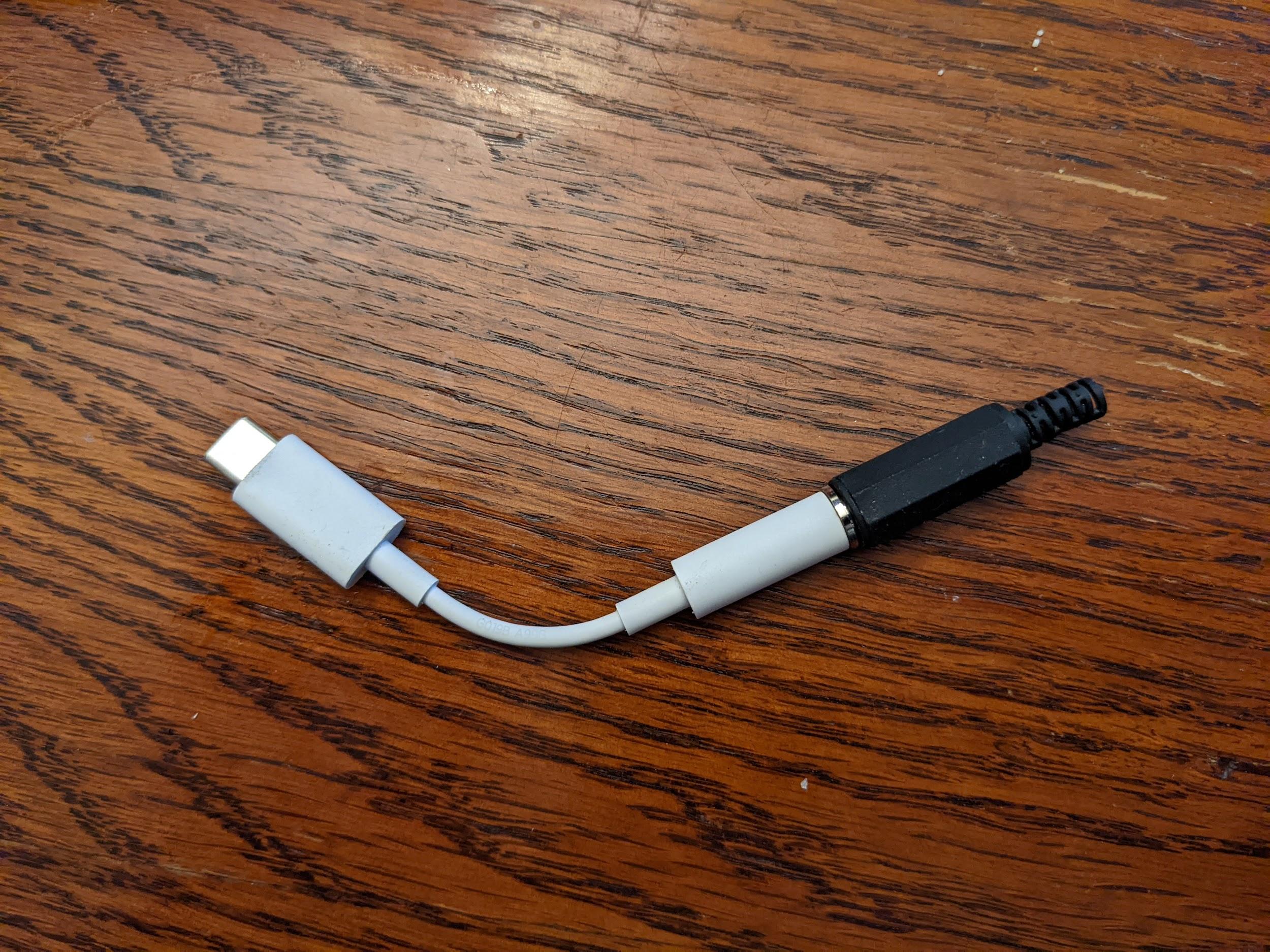

Figure 2. Audio loopback plug connected to USB-to-analog adapter.
The second option is to use a USB audio interface with cables that connect the output to the input.
These instructions are for the Presonus AudioBox USB 96 device:
- Connect the Input 1 connector to Main Out L.
- Connect the Input 2 connector to Main Out R.
- Set the Input 1 knob to straight up.
- Set the Input 2 knob to straight up.
- Set the Phones knob to 0.
- Set the Mixer knob to the far right for Playback.
Set the Main knob to about 45 degrees left of straight up (about 10:30 on a clock face).
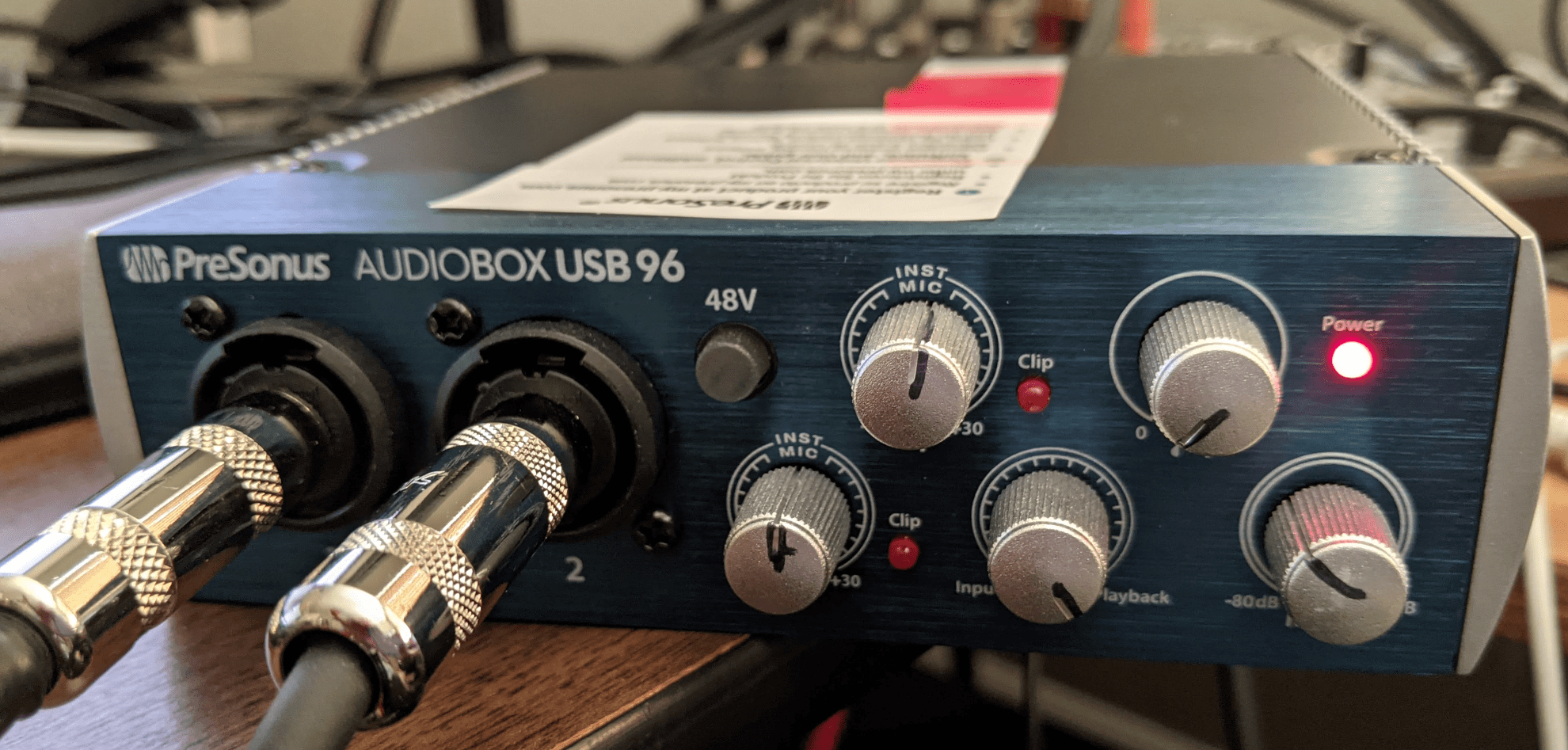

Figure 3. USB audio interface with the correct settings.
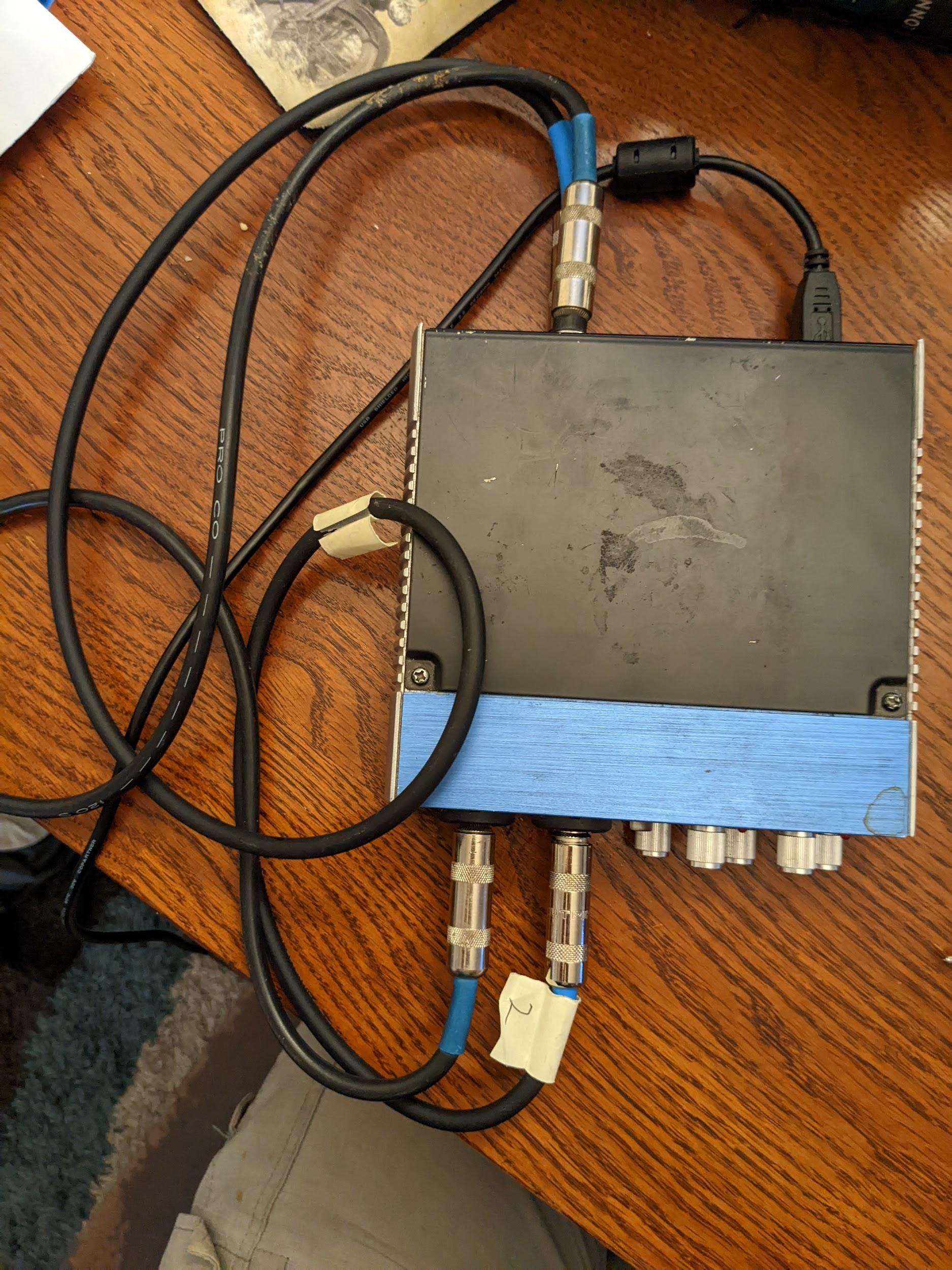

Figure 4. USB audio interface top view with the correct connections.
Run the audio loopback latency test
After setting up your selected peripherals, run the audio loopback latency test to take measurements for the loopback latency on all paths supported by the DUT:
Test the internal speaker to the internal microphone (speaker or mic route):
- Perform this test in a quiet room.
- Place the DUT flat on a table. If the DUT is in a case, you might need to remove that case.
- Tap Start for the speaker or mic route. A series of noise bursts play, and at the end of the test process the results for the speaker or mic route display. You might need to adjust the volume to get a sufficient confidence value.
If the DUT doesn't have an analog headset jack, skip this step. Otherwise, test the analog headset jack:
- Insert the loopback plug into the analog headset jack on the DUT. This activates the Start button for this route.
- Tap Start. The same series of noise bursts is routed through the headset jack and the latency is measured. You might need to adjust the volume to obtain a sufficient confidence value.
If the DUT doesn't have a USB port that implements USB host mode, skip this step. Otherwise, test the USB port:
- Connect the USB loopback device (adapter and loopback plug OR USB interface with appropriate loopback cables) to the DUT.
- Tap Start. The same series of noise bursts are routed through the USB adapter or interface and the latency is measured. You might need to adjust the volume to obtain a sufficient confidence value.
Report the results:
- If all routes meet the criteria listed in the Android CDD, mark the test as passed.
- If any route doesn't meet the criteria, mark the test as failed.
Execute the audio frequency line test
This test uses an audio loopback dongle to characterize the left and right line audio output from the 3.5 mm analog jack. The test uses the mic feedback from the plug to capture audio and compute a frequency response for each channel.
A criterion for minimum energy expected in each band (out of four) is applied for each channel.
To run this test:
- Follow the General instructions to access the test.
Tap YES or NO to report whether the device has a physical headset port. If it doesn't have a physical port, mark the test as passed.
Figure 5. Audio frequency line.
Connect a loopback plug to the headset connector (see Loopback latency test).
Tap LOOPBACK PLUG READY.
Figure 6. Loopback plug ready.
Tap TEST and wait for the test to complete.
When the test is complete, view and the results on the test screen.
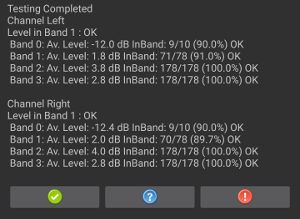
Figure 7. Testing complete.
If the test passed, press the green checkmark. If the test failed, press !.
Run the audio frequency speaker test
This test uses the signal captured by an external USB reference microphone to assess the speakers' frequency response.
A reference microphone delivers a flat, uncolored audio response. These microphones are often used for analysis and measurement equipment.
Minimum recommended reference microphone characteristics:
- Flat frequency response on range 100 Hz to 20 kHz: +/- 2 dB S/N ration 70 dB (A-weighted)
- THD ratio @ 1000 Hz less than 1% at 127 dB SPL
Recommended microphones include the miniDSP USB measurement calibrated microphone and the Dayton Audio UMM-6 USB measurement microphone.
To run the test:
Connect a USB reference microphone to the DUT and place the microphone 20 cm away from the DUT and perpendicular to the center of the screen:
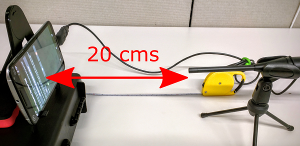
Figure 8. Device under test.
Tap USB REFERENCE MICROPHONE READY.
Figure 9. Microphone ready.
Tap TEST and wait for the test to complete.
When the test is complete, view and the results on the test screen.
If the test passed, press the green checkmark. If the test failed, press !.
Execute the audio frequency microphone test
This test requires both external speakers for a white noise sound source and a USB reference microphone to calibrate the DUT's internal microphone against. The speakers don't need to have a flat frequency response, but they need good coverage from low frequencies (100 Hz) to high frequencies (20 kHz).
To run the test:
Report whether the DUT has a physical audio output port. If it doesn't, mark the test as passed.

Figure 10. Audio microphone test.
Position the speakers 40 cm perpendicular to the center of the screen of the DUT.
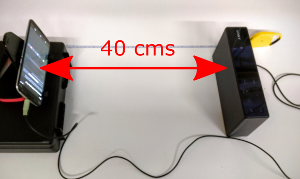
Figure 11. Device under test.
Connect external speakers to the DUT using the headphone or line out connector. Unplug any USB microphone connected to the DUT.
Tap EXTERNAL SPEAKERS READY.
Figure 12. Testing underway.
Tap TEST 1 and wait for the test to complete. When the test is complete, results are shown on the test screen:
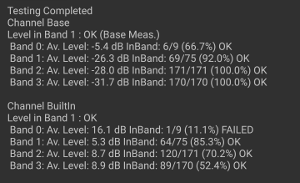
Figure 13. Test results.
Connect a USB reference microphone to the DUT. Keep the external speakers connected and position the microphone next to the DUT's internal microphone, pointed toward the external speakers.

Figure 14. Device position.

Figure 15. Microphone position.
Tap USB REFERENCE MICROPHONE READY.

Figure 16. Microphone ready.
Tap TEST 2 and wait for the test to complete. When the test is complete, results are shown on the test screen:
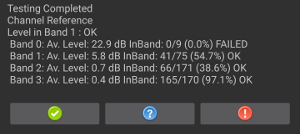
Figure 17. Testing complete.
Record the test results.
Run the audio frequency unprocessed test
This test requires a sound pressure level (SPL) meter in addition to a USB reference microphone and external speakers.
If the DUT has a definition for the Audio Frequency Unprocessed feature, all sections of this test must pass. If the DUT doesn't define this feature, the test can pass even if not all sections pass.
To run the test:
Connect external speakers to the DUT using the headphone or line out connector. Unplug any USB microphone connected to the DUT.

Figure 18. DUT setup.
To conduct the tone test:
- Tap PLAY.
Move the SPL meter in front of the speakers until it detects a sound pressure level of 94 dB SPL.

Figure 19. Test tone setup.
Move the SPL meter back and forth in a straight line from the speakers in a straight line from the speakers. Make a note of this location.
Figure 20. SPL meter placement.
Move the DUT and place the microphone in about the same location found in the previous step.
Tap TEST. The DUT performs a short audio capture and automatically stops the playback. If necessary, you can stop playback by tapping STOP.
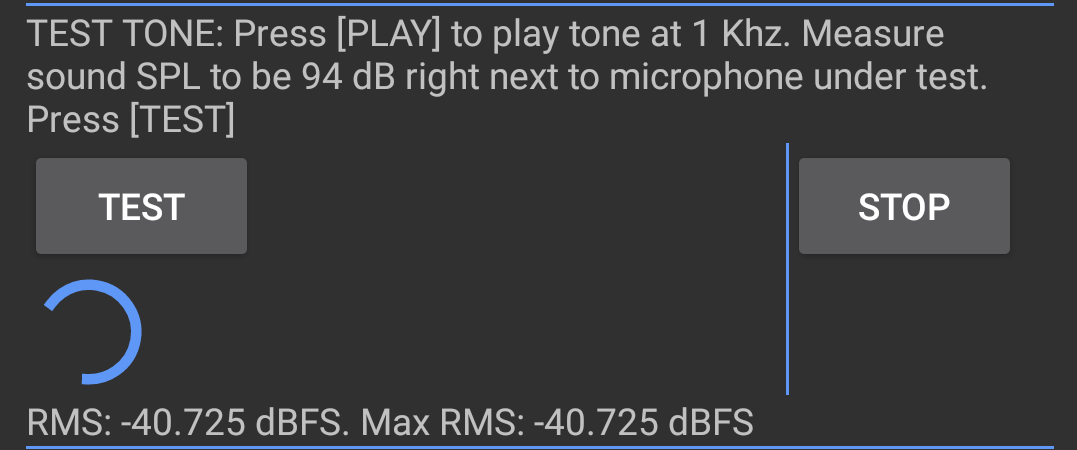
Figure 21. Audio capture.
To conduct the noise test:
Position the speakers perpendicular to the center of the screen of the DUT and 40 cm away.
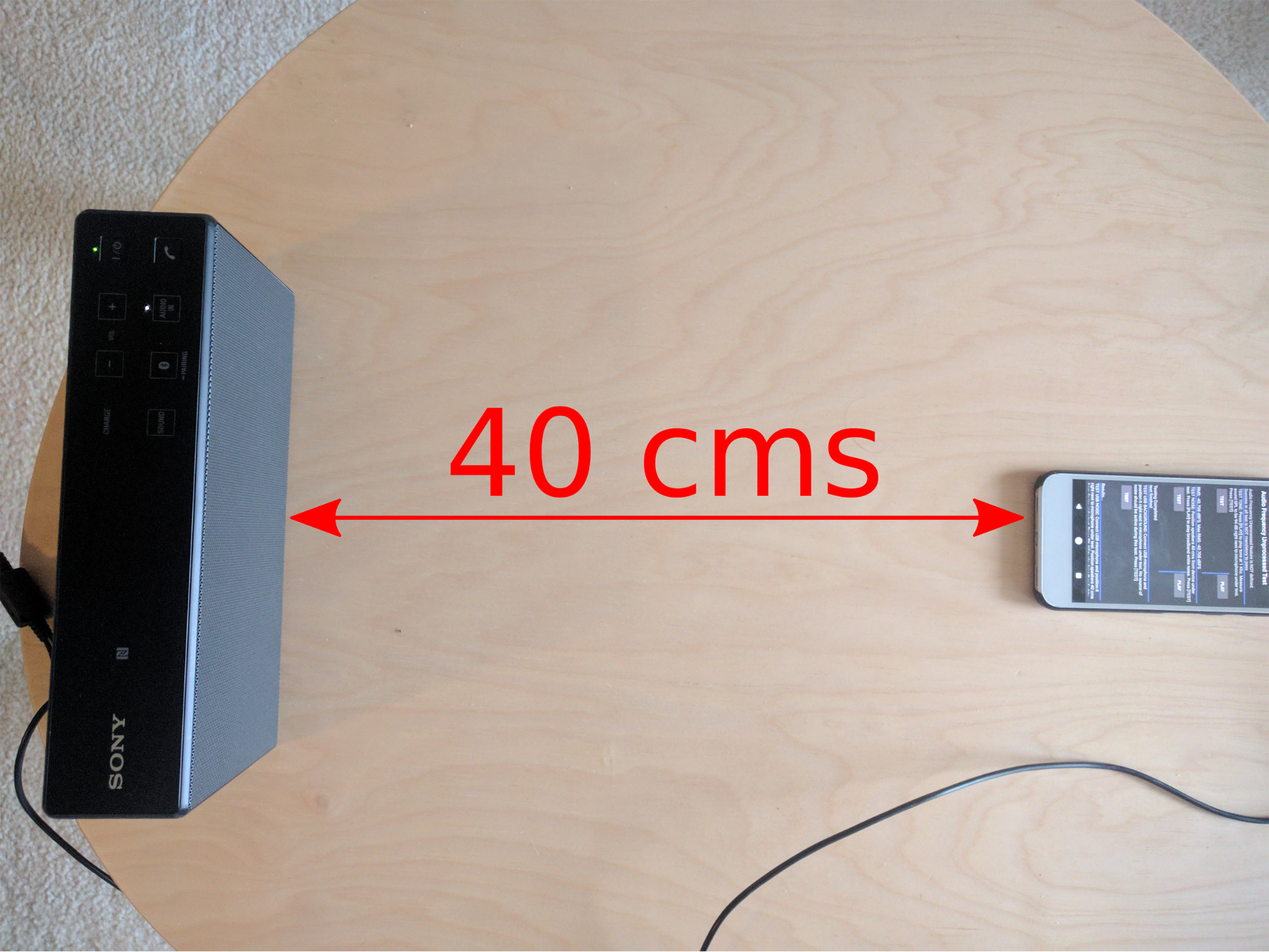

Figure 22. Speaker placement.
Tap PLAY.
Tap TEST and wait for the test to complete. Playback stops automatically when the test is complete.

Figure 23. Running test.
To test USB background:
- Connect a USB Reference microphone to the DUT and position it close to the DUT's internal microphone.
Tap TEST. The test runs and displays results on screen.

Figure 24. USB reference microphone.
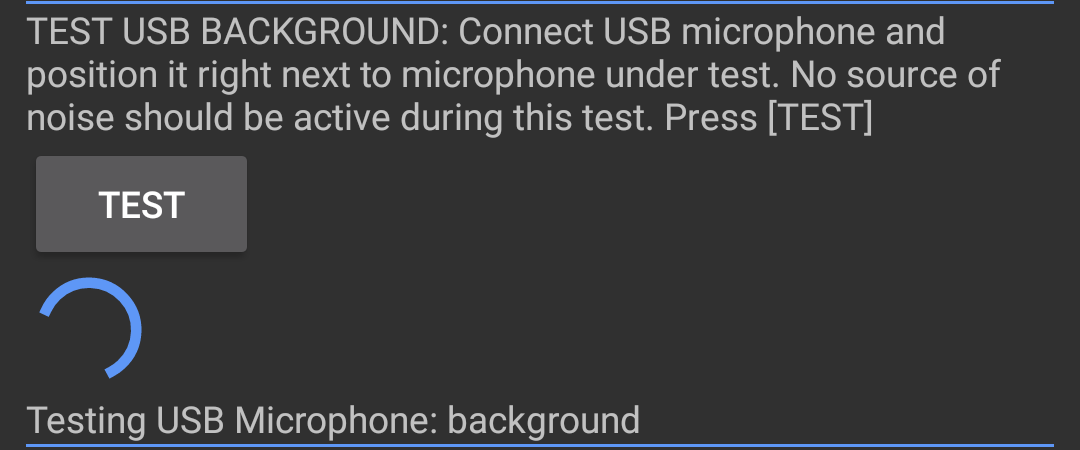
Figure 25. Running test.
To test USB noise:
- Place a USB microphone in the same position as in the previous test.
- Tap PLAY. The speakers play broadband noise.
- Tap TEST. The test runs and displays results on screen.
View the results for all four sections of the test. Repeat sections as needed.
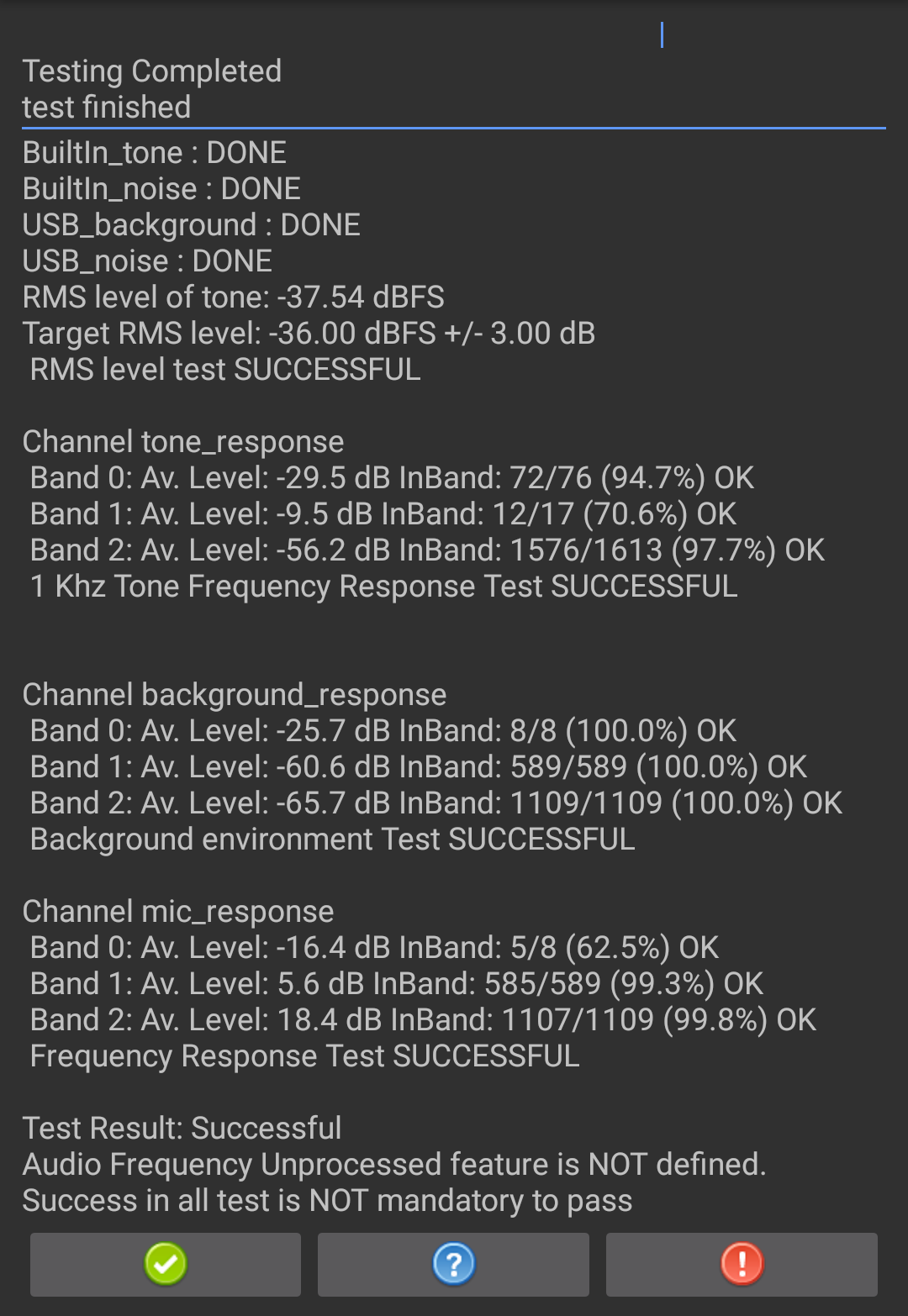
Figure 26. Test results.
If the test passed, press the green checkmark. If the test failed, press !.
